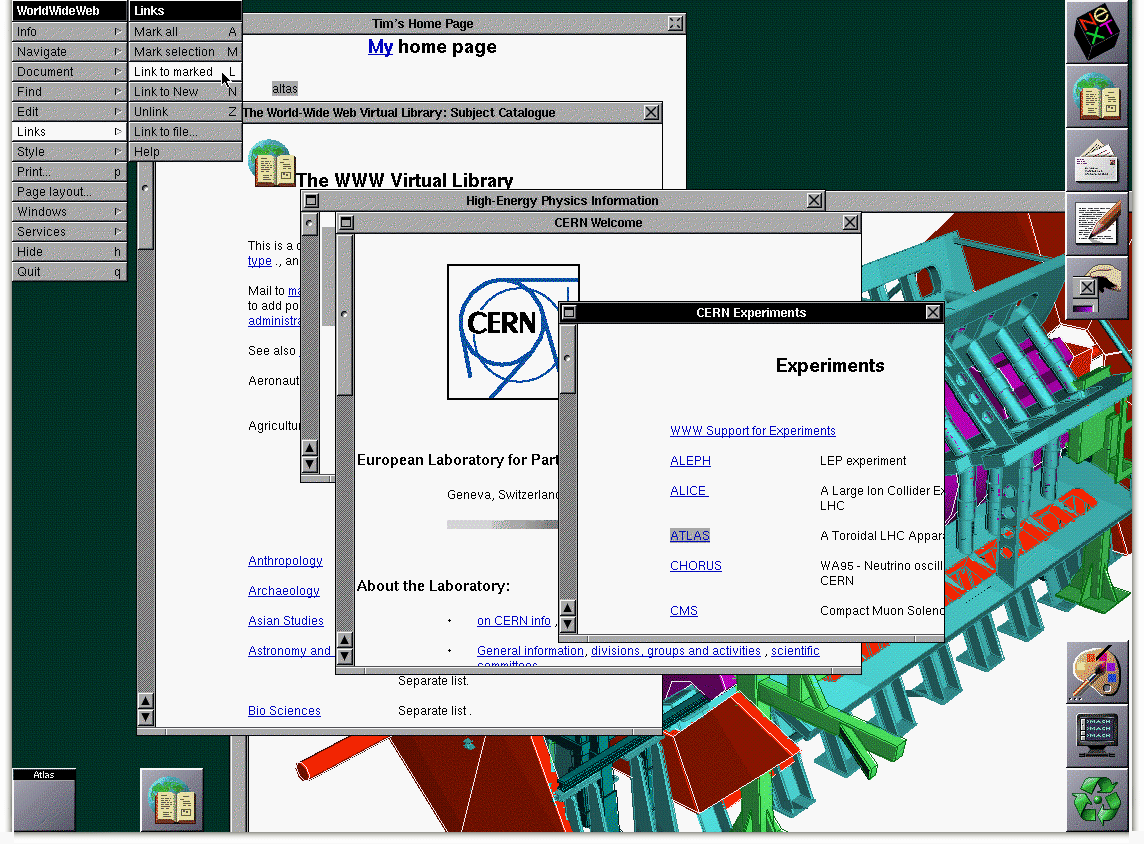
The World Wide Web, WWW, invented by British Physicist, Tim Berners-Lee, in 1989, while working at CERN, was made public twenty years back. Royalty-free WWW launched on April 30, 1993. It “was originally conceived and developed to meet the demand for information sharing between physicists in universities and institutes around the world.”

The CERN has made the first URL public, advising people to take five minutes to browse through it. In a statement by Rolf Heuer, CERN Director-General, he said, “There is no sector of society that has not been transformed by the invention, in a physics laboratory, of the web. From research to business and education, the web has been reshaping the way we communicate, work, innovate and live. The web is a powerful example of the way that basic research benefits humankind.”
According to the CERN, “In 1989 the internet was already a mature set of protocols that enabled data to be transferred between and within different networks in small ‘packets’. The internet was used as a foundation for uses such as email and file transfer systems such as the then-popular Gopher. A community of enthusiasts was sharing ideas on how to create “hypertext” systems that featured links between documents. HyperCard for the Apple Macintosh was a popular early example of a working hypertext system that featured links between ‘cards'”.
“With WorldWideWeb, Berners-Lee used the internet to create a networked hypertext system that allowed CERN physicists to read and publish documents, and to create links between and within them.”
“On 30 April 1993, CERN made the source code of WorldWideWeb available on a royalty-free basis; the software was free for anyone to use, and remains so today. Web usage exploded as people started setting up their own servers and websites. By late 1993 there were over 500 known web servers, and the WWW accounted for 1% of internet traffic, which seemed a lot in those days (the rest was remote access, e-mail and file transfer). Twenty years on, there are an estimated 630 million websites online.”