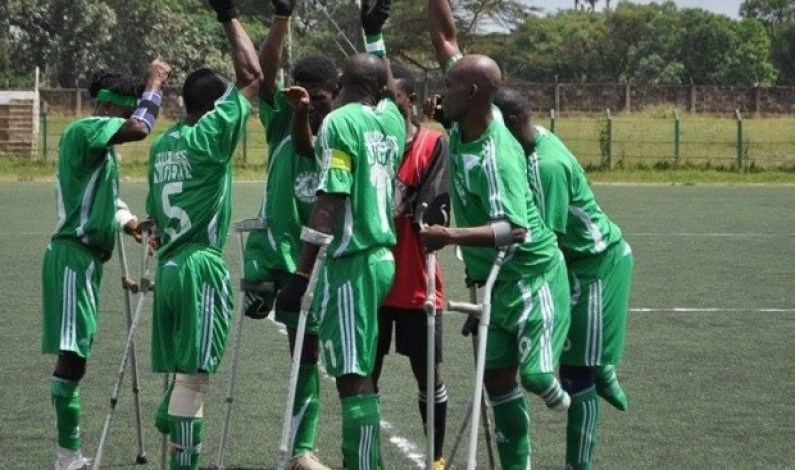
In a bid to help the Nigeria Amputee Football team make it to the
Mexico 2018 Amputee World Cup, set to hold from October 24th to November 5th, Haggai Sports, a Nigerian sport
kits company, in collaboration with the Nigeria Amputee Football Federation (NAFF), has launched a jersey sales campaign.
The fundraiser is aimed at enlightening the public on the importance of amputee football, while also soliciting their financial support through the purchase of the team jersey from which a percentage will count as part of the ₦30 million needed to cover the flight ticket, visa fees and upkeep of 15 players and five officials to the event.
This initiative became imperative following NAFF’s abandonment by the government after many months of appeals.
President of NAFF, Isah Suleiman, said Nigeria missed out on three editions of the world cup despite qualifying, and this has greatly demoralised the team who look forward to representing their country in Mexico this year.
“We have been appealing to the authorities and various corporate bodies for help but yet to no avail, so we decided on this creative way, while still hoping and praying that the government and corporate institutions would eventually come.
“The company kitting the team for free, agreed to further remit 20% of the purchase price for each jersey bought by the public, to the Amputee team to help generate the needed fund.”
— Suleiman
The price of each quality jersey is ₦5,000 with ₦1,000 for delivery to any destination in Nigeria.
You might also like:
This article was first published on 2nd October 2018
Notice: Undefined variable: last_modified in /var/www/html/articles/wp-content/themes/cnhalptem/content-single.php on line 36
achem
Achem Samuel is a writer and a musician, he is passionate about God and also an ardent fan of tech, sports and music.
Comments (0)